Supply Curve Shift Left
Likewise at point H the rate of interest is higher than at F. In Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply a reduction in supply is shown as a shift of the supply curve to the left.

Does This Explanation Pertaining To The Supply Curve And Law Of Supply Make Sense Economics Stack Exchange
The demand curve is downward sloping from left to right depicting an inverse relationship between the price of the product and quantity demanded.

. Like changes in aggregate demand changes in aggregate. The law of supply and demand is the theory explaining the interaction between the supply of a resource and the demand for that resource. The supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied for a.
The supply curve either moves left or right horizontally since the prices stay the same and only the quantities change and quantity is on the horizontal axis. That would show up in Example 1 above if the demand curve is drawn flatter more elastic. Higher costs of production.
The movement in demand curve occurs due to the change in the price of the commodity whereas the shift in demand curve is because of the change in one or more factors other than the price. Then the aggregate demand curve would shift to the left. 384 clearly shows that points above and to the right of the IS curve like H are points of excess supply of goods ESG.
Shift In Supply Curve. If government were to cut spending to reduce a budget deficit the aggregate demand curve would shift to the left. The demand curve does not shift because none of the factors affecting demand have changed.
However in this situation the horizontal axis represents the quantity of product or service demanded. By contrast points below and to the left of the IS curve are points of excess demand for goods EDG. Therefore for any given price producers are willing and able to supply more hamburgers.
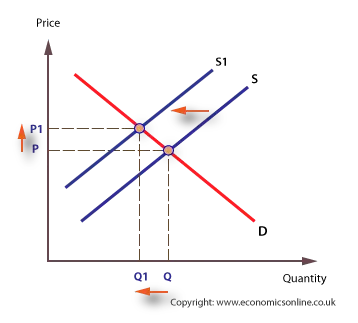
A shift to the left of the SAS curve from SAS 1 to SAS 3 or of the LAS curve from LAS 1 to LAS 3 means that at the same price levels the quantity supplied of real GDP has decreased. Those factors include 1 number of sellers 2 prices of other goods 3 prices of input 4 technology 5 expectations about prices. Unlike the supply curve the demand curve moves downward from left to right.
There are a number of factors that cause a shift in the supply curve. For example a large shift of the supply curve can have a relatively small effect on price if the corresponding demand curve is elastic. Negative supply shock-stagflation-a negative shift that leads to a higher aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the left.
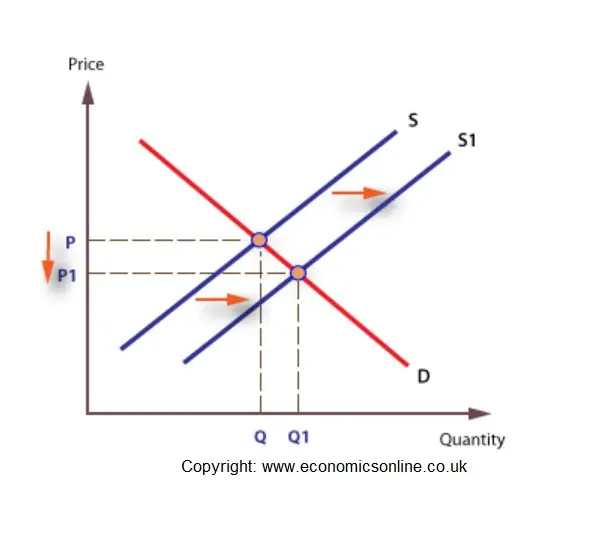
In this case the new equilibrium price falls from 6 per pound to 5 per pound. This has led an increase in quantity Q1 to Q2 but price has stayed the same. In this diagram supply and demand have shifted to the right.
Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. The left-ward shift of the supply curve is caused by two factors expectations and prices of input. If firms in a perfectly competitive industry are earning losses we would expect that in the long run the market demand curve for the product will shift to the left causing industry output to fall.
The supply curve may shift to the left because of. Elasticity here refers to demand being sensitive to price Sensitive To Price Price Sensitivity also known and calculated by Price Elasticity of Demand is a measure of change in percentage term in the demand of the product or service compared to. In this case the supply curve shift to left initially S 1 to S 2.
Demand can be elastic or inelastic. When the shift moves towards the left it indicates a decrease in the number of the products supplied. There are various non-price determinants that occur shift in supply curve.
The law of supply and demand. Similar to the supply curve it includes vertical and horizontal axes. Suppose interest rates were to fall so that investors increased their investment spending.
On the other hand if the shift is. Move the short-run aggregate supply SRAS curve andor the aggregate demand AD curve in the accompanying graph to demonstrate a negative supply shock. The demand curve correlates goods demand at various price levels.
The innovation in meat processing technology lowers the cost of producing hamburgers. An increase in supply results in an outward shift of the supply curve ie. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.
Input prices number of sellers technology natural and social factors as well as expectations. The market supply curve for the product will shift to the left causing industry output to fall. The market supply curve for the product will shift to the right causing industry output to rise.
Law Of Supply And Demand. When the entire market scenario is depicted via this curve it is referred to as a market supply curve. Supply and Demand Shift Right.
There is a range of different factors that cause a supply curve to shift either left or left. Two forces contribute to the size of a price change. The equilibrium price also increases from the point of intersection of P1 and Q1 to another intersection of P2 and Q2 eventually the equilibrium price had been increased.
That showcases the law of demand wherein the demand decreases as the price increases. If they decide they want more goods and services the supply curve is likely to shift to the right. This leads to a rightward shift in the supply curve.
A change in attitudes toward work and leisure can shift the supply curve for labor. If the shift to the left of the supply curve is greater than that of the demand curve the equilibrium price will be higher than it was before as shown in Panel b. In this case the new equilibrium price rises to.
And there is excess supply of goods ESG. -AD curve shifts to the left Positive supply shock. The amount of the shift and the elasticity of demand or supply.
We must know how they shift the supply curve if we are to use the supply and demand tool to understand how prices are determined in a market economy. To the right whereas a decrease in supply results in an inward shift ie. If people decide they value leisure more highly they will work fewer hours at each wage and the supply curve for labor will shift to the left.
The aggregate demand curve would shift to the right.

B Market Equilibrium Demand And Supply Microeconomics Ind Assignment
What Causes A Shift In The Supply Curve Quora
0 Response to "Supply Curve Shift Left"
Post a Comment